Introduction
In today’s internet, bots, fake traffic, and automated attacks make up a massive portion of online activity, and that’s where CAPTCHAs come in. These small but powerful tests are how websites keep human users separate from machines, protecting online security and preventing misuse of forms, logins, and data. But what is CAPTCHA, really, and how does it work in an age where AI can solve puzzles faster than people to prevent scammers? In this guide, we’ll unpack the true CAPTCHA meaning, explore its evolution, and show how modern tools like Browserless now help developers solve CAPTCHAs ethically, efficiently, and in full compliance with security best practices.
What is CAPTCHA?
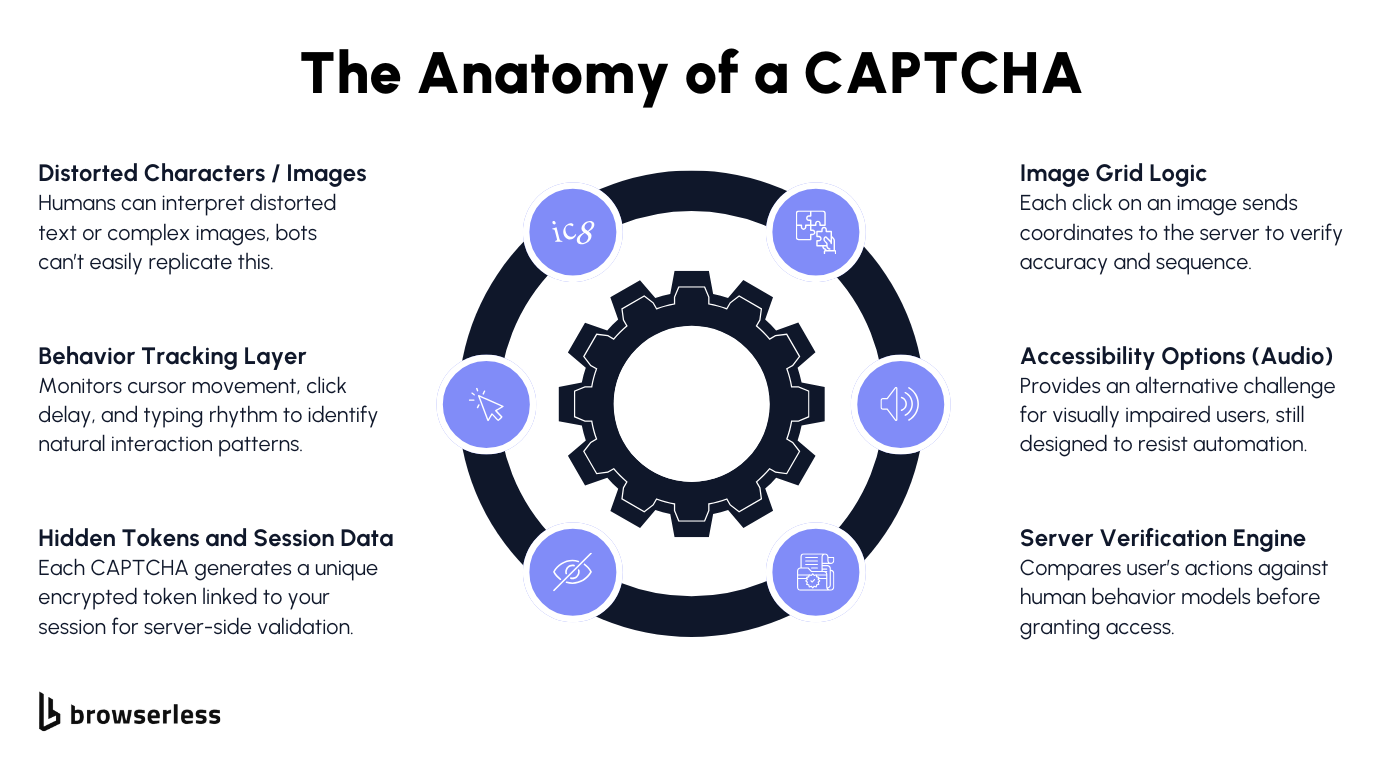
The Meaning Behind CAPTCHA
If you’ve ever had to type out a string of distorted text or click every square showing traffic lights, you’ve already completed a CAPTCHA test, a quick way for websites to check if you’re human. The term CAPTCHA stands for Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart, and it does exactly that.
Created at Carnegie Mellon University in the early 2000s, it was designed as a security measure to stop bots from flooding web forms, contact forms, and website registrations with spam, junk mail, and fake accounts.
By presenting users with a small challenge, such as typing letters into a text box or solving a visual puzzle, sites can ensure that only legitimate users gain access to their services.
In its earliest form, CAPTCHA technology used text-based CAPTCHAs, showing a distorted image or a jumble of distorted characters that required users to rely on human intelligence to interpret. This simple idea worked because computers, or more accurately, automated scripts, weren’t yet good at understanding images or irregular text.
It was a clever way to prevent bots from abusing free services, flooding comment sections with false comments, or submitting dictionary attacks.
Over time, however, machine learning and optical character recognition began catching up, making these traditional CAPTCHA less effective. That shift pushed the industry toward smarter, more user-friendly CAPTCHA systems that continue to protect online services today.
How CAPTCHA Evolved
As the internet grew, CAPTCHA had to evolve, too. The old text-based CAPTCHA tests, once clever, began to frustrate users, particularly those who are visually impaired or blind and struggle to interpret the CAPTCHA image.
To make things more inclusive, developers introduced audio CAPTCHAs, an audio version that reads characters aloud for those using screen readers or experiencing impaired vision.
Later came image-based CAPTCHA, which asked users to pick photos containing traffic lights, buses, or storefronts, simple tasks that rely on image recognition and human reasoning that bots still can’t match.
But perhaps the biggest leap forward came with Google’s CAPTCHA reCAPTCHA, a next-generation approach that made the CAPTCHA challenges almost invisible. Modern versions like reCAPTCHA v2 and v3 rely on advanced risk analysis techniques that track aspects such as mouse movement and user behavior in real time.
Instead of presenting users with a puzzle, these systems quietly decide whether you’re human based on how you move, click, and scroll. This background analysis enables CAPTCHA to function seamlessly for legitimate users while preventing malicious bots from accessing protected web pages and form fields. It’s a perfect example of how CAPTCHA technology continues to evolve, protecting the internet while staying one step ahead of attackers.
Common Types of CAPTCHA
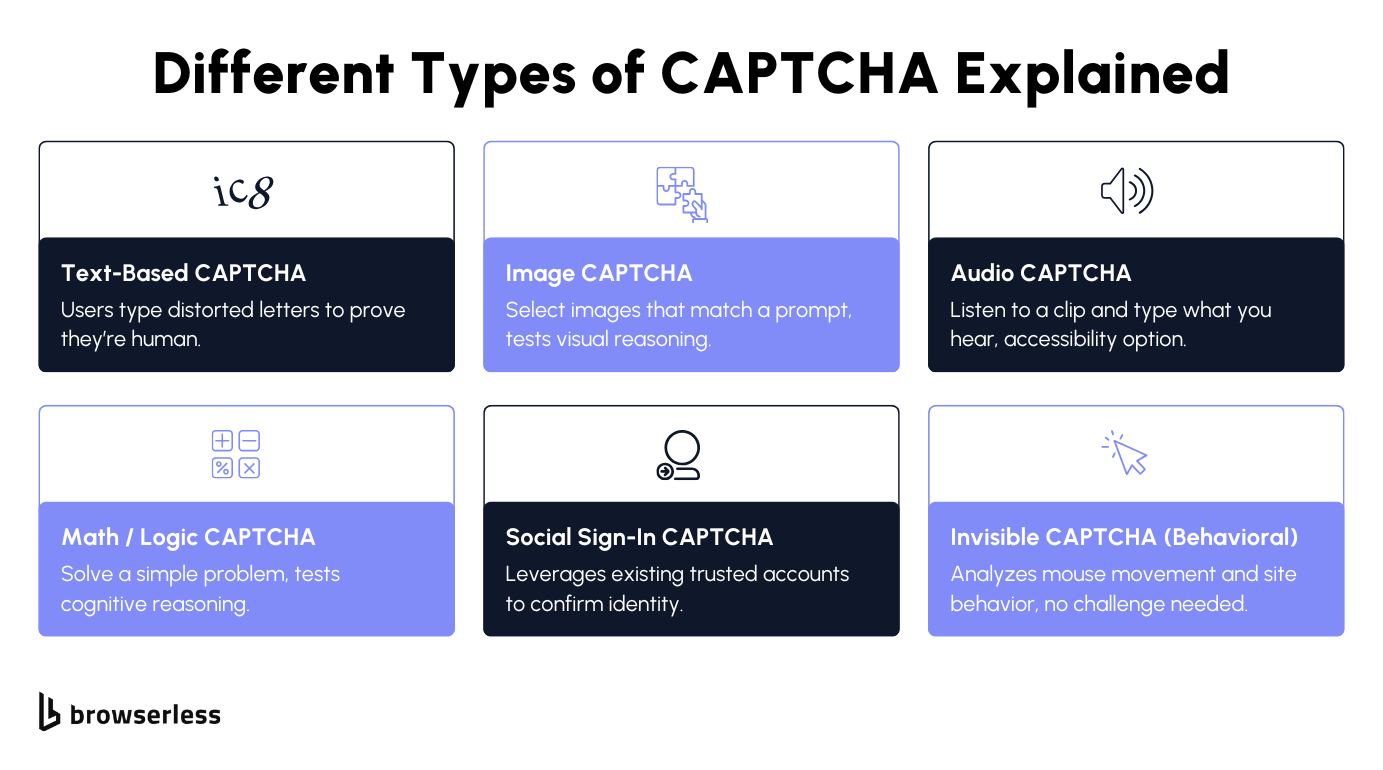
Every time you verify you’re not a robot by typing distorted text, clicking traffic lights, or solving a small puzzle, you’re taking a CAPTCHA test, including reCAPTCHA.
These challenges, short for Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart, protect web pages, web forms, and online services from bots, spam, and automated scripts.
Each CAPTCHA type uses a different method to separate human users from machines, ensuring only legitimate users can gain access to a protected resource.
- Text-Based CAPTCHA – The classic CAPTCHA image that displays distorted characters users must type into a text box. It prevents bots and fake accounts by defeating optical character recognition systems.
- Image CAPTCHA – An image-based CAPTCHA asking users to identify objects like traffic lights or buses, testing image recognition and human intelligence.
- Audio CAPTCHA – An audio version for visually impaired users and blind users, where users type what they hear from a distorted clip.
- Math / Logic CAPTCHA – Requires solving small word problems or equations, testing reasoning that bots can’t easily mimic.
- Social Sign-In CAPTCHA – Uses existing accounts to verify legitimate users, simplifying login while maintaining security measures.
- Invisible CAPTCHA (Behavioral) – Modern CAPTCHA technology, such as reCAPTCHA v3, uses advanced risk analysis techniques to monitor mouse movement, clicks, and timing, confirming real activity without presenting users with a puzzle.
CAPTCHA Use Cases
You’ve likely seen CAPTCHA challenges everywhere, from text-based CAPTCHAs with distorted images to image CAPTCHAs that make you select photos of traffic lights or crosswalks. These are everyday examples of how CAPTCHA systems quietly protect online services from abuse.
Each captcha test relies on human perception and logic, things that machine learning models and automated scripts still struggle to imitate. Whether you’re identifying shapes, typing captcha codes, or checking “I’m not a robot,” you’re helping websites tell computers and humans apart in real time.
What makes these systems powerful is how CAPTCHA works behind the scenes. By analyzing how users type, click, and move, modern CAPTCHA technology detects patterns unique to real users.
Tools like reCAPTCHA use advanced risk analysis techniques to silently filter bots, protecting web pages, contact forms, and website registrations from spam, false comments, and malicious activities.
It’s a simple concept that continues to evolve, keeping the web secure for only legitimate users while ensuring accessibility for visually impaired users through audio CAPTCHA.
Where CAPTCHA Is Used
CAPTCHA appears everywhere on account creation pages, login portals, payment gateways, and online polls, acting as a crucial security measure for web forms. They prevent bots from generating spam, submitting fake accounts, or posting false comments, helping maintain poll accuracy and the quality of online services. Even message boards and contact forms rely on traditional CAPTCHA to reduce junk mail and dictionary attacks that target web pages daily.
Businesses in e-commerce, fintech, and SaaS depend on CAPTCHA systems to protect sensitive form fields and website registrations from abuse. Whether through text-based CAPTCHAs, audio CAPTCHAs, or invisible behavioral systems, CAPTCHA works to prevent bots, ensure legitimate users can gain access, and secure every protected resource online.
By blending human intelligence with advanced CAPTCHA technology, these tests remain the quiet defenders of modern web security, keeping the balance between usability, safety, and trust.
How Does CAPTCHA Work?
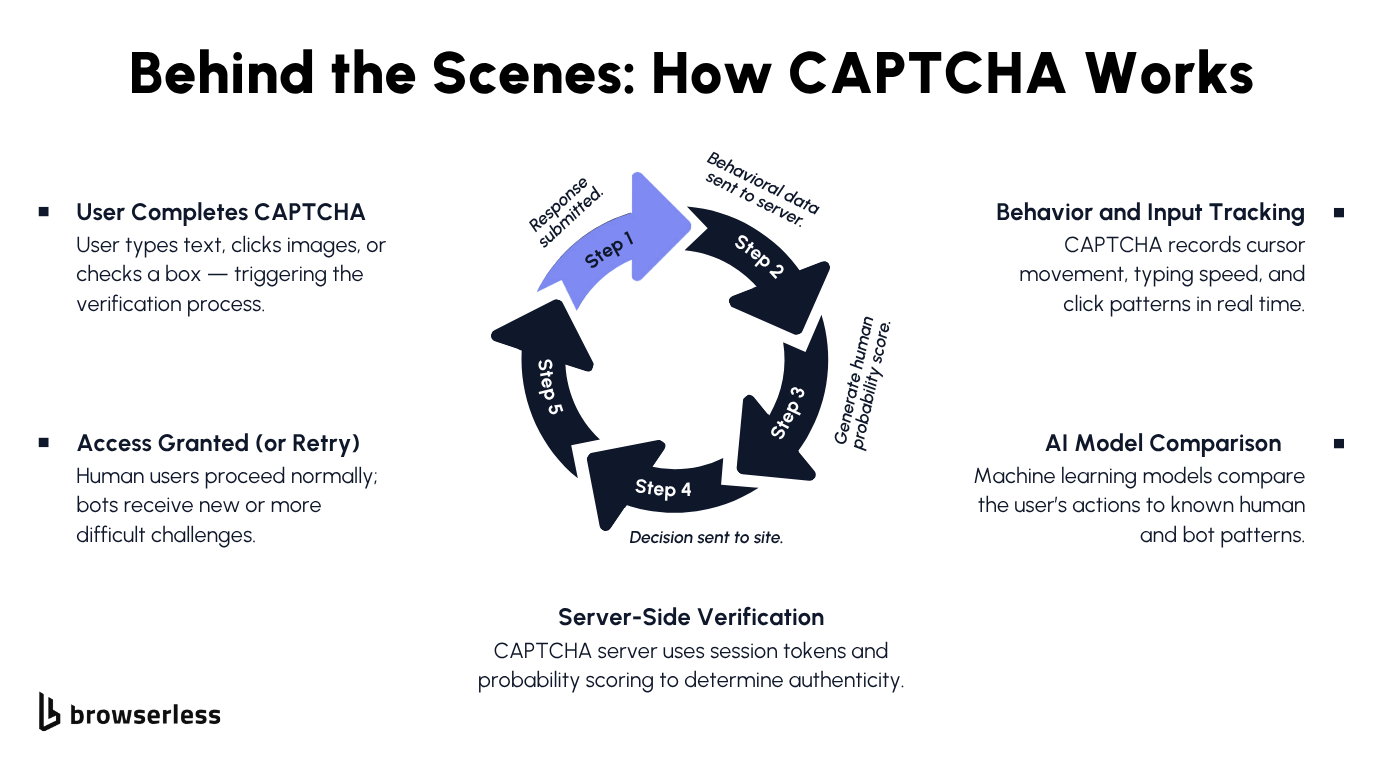
The Process of CAPTCHA Verification
Every time you type in a CAPTCHA code, select images of traffic lights, or listen to an audio CAPTCHA reading distorted words, you’re taking part in one of the web’s simplest but smartest security ideas, the Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart.
That’s a mouthful, but the idea is simple: make a challenge that human users can solve easily while automated scripts can’t. This small security measure helps keep web pages, web forms, and online services safe from spam, fake accounts, and other malicious activities.
Here’s how a CAPTCHA test really works behind the scenes:
- The website presents a challenge. When you try to log in or submit a form, the system may detect possible automation and show a CAPTCHA challenge, which could be a text-based CAPTCHA, an image CAPTCHA, or even an audio version for visually impaired users or blind users.
- You respond. You might type letters from a distorted image into a text box, pick all the squares with traffic lights, or listen to an audio clip and type what you hear.
- The system checks your answer. The server verifies your input using algorithms that filter out optical character recognition attempts from bots and look for genuine human intelligence behind the response.
- Behavioral scoring kicks in. Modern CAPTCHA systems do more than check answers; they analyze mouse movement, timing, and your interaction with the page. These subtle signals help confirm that you’re a real user, not a script.
- Verification and access. If your activity looks natural, you’re cleared instantly; only legitimate users get through. If not, the site may add more CAPTCHA challenges or block access entirely, protecting the protected resource behind it.
What’s amazing is that this whole process takes seconds. CAPTCHA technology quietly verifies your authenticity so you can gain access while bots get filtered out, all to keep your favorite online services secure and spam-free.
Smarter Bots, Smarter CAPTCHA
Of course, as bots get smarter, CAPTCHA S have to evolve too. Early text-based CAPTCHA S with distorted characters worked well when bots were simple, but machine learning and image recognition have changed the game. Some automated scripts can now solve image CAPTCHAs or bypass audio CAPTCHAs, forcing websites to rethink how CAPTCHAs work in the age of AI.
That’s where modern systems like reCAPTCHA v3 come in. Instead of always presenting users with puzzles, these invisible CAPTCHAs use advanced risk analysis techniques and AI-driven behavior tracking.
They quietly observe how you scroll, move your mouse, and interact with web pages, assigning a trust score based on those patterns. If everything looks normal, you’ll never even see a challenge. But if something seems off, like automated clicking or suspicious timing, the system raises the difficulty or blocks the request altogether.
Today’s CAPTCHA technology strikes a balance between security and experience. It ensures only legitimate users can pass through, without interrupting every visit with a CAPTCHA test. It’s a small but brilliant way the web keeps computers and humans apart, letting real users move freely while keeping the bots at bay.
Solving CAPTCHA: How Browserless Makes It Seamless

The Automation Problem: Why CAPTCHA Breaks Bots and Scripts
If you’ve ever automated a login, web scrape, or integration, you’ve likely hit a CAPTCHA test at the worst possible moment. It’s frustrating when your workflow stops cold, with no easy fix.
But CAPTCHAs exist for a reason: it protects web pages and online services from bots, spam, email worms, and fake accounts, keeping human users safe. They’re not meant to punish developers to prevent bots and other malicious activities.
Still, for automation, CAPTCHA can be a headache. Many attempt quick fixes, such as CAPTCHA bypass APIs or outsourced solvers, but these methods are risky and often unethical.
They can violate site policies, expose data, and break compliance. The real challenge isn’t avoiding CAPTCHAs, it’s learning to solve CAPTCHAs responsibly. That’s where Browserless steps in, offering a smarter, compliant path for CAPTCHA automation.
How Browserless Solves CAPTCHA the Right Way
Browserless provides developers with an ethical, built-in solution to handle CAPTCHA without disrupting automation. The Browserless.solveCaptcha() function automatically detects and processes CAPTCHA events during scripts, so you don’t have to stop or rewrite workflows. It even supports Hybrid Automation, allowing a human to step in during critical actions like login or 2FA.
Here’s a quick example of how simple it is to integrate CAPTCHA solving into your automation workflow using Browserless:
import puppeteer from "puppeteer-core";
const run = async () => {
// Connect to Browserless using your API token
const browser = await puppeteer.connect({
browserWSEndpoint: "wss://production-sfo.browserless.io?token=YOUR_API_KEY",
});
const page = await browser.newPage();
await page.goto("https://www.google.com/recaptcha/api2/demo");
const cdp = await page.createCDPSession();
// Solve any CAPTCHA on the page
const { solved, error } = await cdp.send("Browserless.solveCaptcha");
console.log({
solved,
error,
});
await browser.close();
};
run();
In just a few lines of code, Browserless handles the entire CAPTCHA test process, detecting, solving, and continuing the flow automatically. Meanwhile, Stealth Mode mimics natural mouse movement, clicks, and human timing to avoid detection while keeping sessions secure.
Instead of relying on shady workarounds or brittle scripts, Browserless CAPTCHA automation works with modern CAPTCHA technology and CAPTCHA systems, not against them. It ensures that only legitimate users pass through safely, enabling developers to automate ethically, efficiently, and in full compliance, thereby keeping workflows stable and future-proof.
Automatic Solving
For automatic captcha solving, you can send &solveCaptchas=true as a query parameter in your connection URL. This will automatically monitor sessions for CAPTCHA challenges and solve them in real-time, firing CDP events for programmatic monitoring. We have full code snippets on automatic captcha solving if you're interested in reading more docs on this.
Conclusion
Even as bots become more advanced, CAPTCHA automation remains one of the web’s most vital defenses, balancing protection, privacy, and usability. The future of CAPTCHA isn’t about blocking automation entirely but refining it: ensuring security systems keep out attackers while still letting real innovation flow. That’s exactly what Browserless CAPTCHA solving represents: a more innovative, more ethical way to automate. With its built-in CAPTCHA handling and stealth automation tools, Browserless helps developers build faster, safer, and more responsible workflows. Explore Browserless’s CAPTCHA automation features today and future-proof your automation stack for the next generation of AI-driven web security.
FAQs
Are CAPTCHAS still effective against bots today?
Yes. While text-based CAPTCHAs and image CAPTCHAs are now easier for bots using machine learning and image recognition, advanced CAPTCHA systems like reCAPTCHA v3 use risk analysis techniques and mouse movement tracking to verify real users. Modern CAPTCHA technology still helps prevent bots and protect online services.
How does CAPTCHA help visually impaired users?
Most CAPTCHA systems include an audio CAPTCHA or an audio version of the CAPTCHA test for visually impaired users and blind users. These allow everyone to verify identity and gain access safely, ensuring only legitimate users can complete web forms or contact forms.
Do CAPTCHA affect user experience?
They can. Older traditional CAPTCHA systems with distorted text or images frustrate human users, whereas modern CAPTCHA technology, such as reCAPTCHA, employs advanced risk analysis techniques to test behavior invisibly. This keeps computers and humans apart without disrupting legitimate users.
What happens if a website doesn’t use CAPTCHA?
Without CAPTCHA, web pages are vulnerable to spam, fake accounts, and automated scripts that flood contact forms, online polls, and message boards. Simple CAPTCHA challenges, such as text-based or image-based CAPTCHA, help prevent bots and protect all protected resources from abuse.
How is AI changing CAPTCHA technology?
AI makes CAPTCHA challenges smarter. As machine learning improves, modern CAPTCHA technology now verifies human intelligence and behavior patterns such as mouse movement or click timing rather than just solving puzzles. This evolution ensures that CAPTCHA works silently to secure online services while keeping real users in flow.