Introduction
Browsers are rapidly evolving from static tools into intelligent assistants that can search, summarize, and automate actions across the web, much like how Google revolutionized online searching. New AI-powered browsers like Perplexity’s Comet, Opera Aria, Brave Leo, and Fellou are leading this shift by combining large language models with real-time web access to deliver conversational answers, generate insights, and perform automated workflows. In this article, you’ll learn how these next-generation browsers work, what makes them different from traditional ones, and how the underlying technologies like automation, scraping, and cloud browser APIs are shaping the future of intelligent web interaction.
What Is an AI Browser (and How Does It Actually Work)?
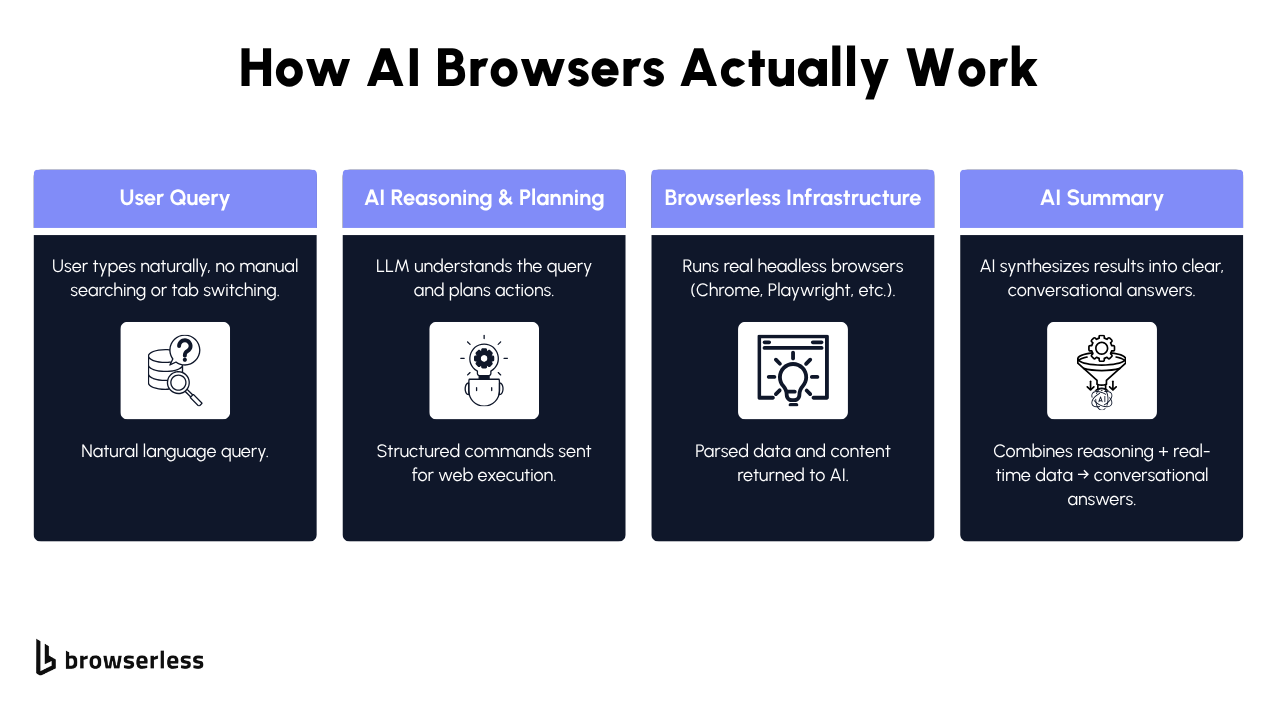
If you’ve used a modern browser lately, you’ve probably noticed something changing. Browsers are no longer passive tools for opening tabs or typing in search bars; they’re turning into active, intelligent companions.
An AI browser can understand what you want, find answers, summarize web pages, and even perform actions on your user's behalf. It’s not just another browser you use for scrolling or saving bookmarks. It’s closer to having a personal AI assistant that helps with everyday tasks, from doing research to comparing products or even drafting messages.
These systems merge traditional web access with AI features that interpret intent, automate workflows, and keep context across sessions, all while maintaining speed, security, and accuracy.
Understanding AI Browsers: When Search Meets Intelligence
An AI browser is designed to understand what you mean, not just the words you type. Instead of giving you a page of links, it reads, reasons, and responds directly.
For example, Perplexity’s AI browser can pull live information, summarize it clearly, and reference the sites it used. Others, like Brave Leo, Microsoft Edge’s Copilot, and Opera Aria, bring conversational and automation layers right inside the browsing experience.
Here’s a closer look at what’s happening under the hood:
- LLM-based query interpretation – The browser converts natural language into structured commands, like “find customer reviews,” “summarize this article,” or “save this webpage.”
- Real-time crawling and scraping – This gives the browser live access to the internet, so it pulls accurate, up-to-date data instead of old cached results.
- On-page context parsing – Using DOM and JavaScript analysis, the browser reads and extracts information directly from the webpage, understanding what’s relevant based on your request.
These systems work together to make AI browsing feel intuitive while running a technically complex process behind the scenes. You can talk naturally to your AI assistant, and it handles the rest, fetching content, saving useful links, or helping you make sense of detailed information with a few words.
How AI Browsers Think and Act Like Humans Online
AI browsers go a step further than traditional automation. They actually perform actions across the web the same way a human user would. They can scroll, click links, fill out forms, and read dynamically generated pages with a single click, something traditional browsers couldn’t do automatically. Using frameworks like Playwright, Chrome, and Edge, they can execute real browser actions and react to live content in real time.
Behind that behavior are systems built to manage complex tasks efficiently. Session management keeps credentials, passwords, and cookies active, allowing the browser to stay signed in securely while keeping data encrypted.
Dynamic rendering enables it to handle JavaScript-heavy sites by loading every visual and interactive element you’d normally see. To maintain reliability, many AI browsers introduce subtle human-like patterns, delays between actions, realistic scrolling, or cursor movements to avoid being flagged by automated detection systems.
Modern AI browsers can now help with far more than search. You can create images, compare specs for a purchase, or even have it summarize long reports, allowing you to focus on other work.
Some users are already replacing multiple apps with their browser alone, using it to collect research, manage tabs, or even send emails directly from a sidebar.
The Role of Browser Automation in Making AI Browsers Possible
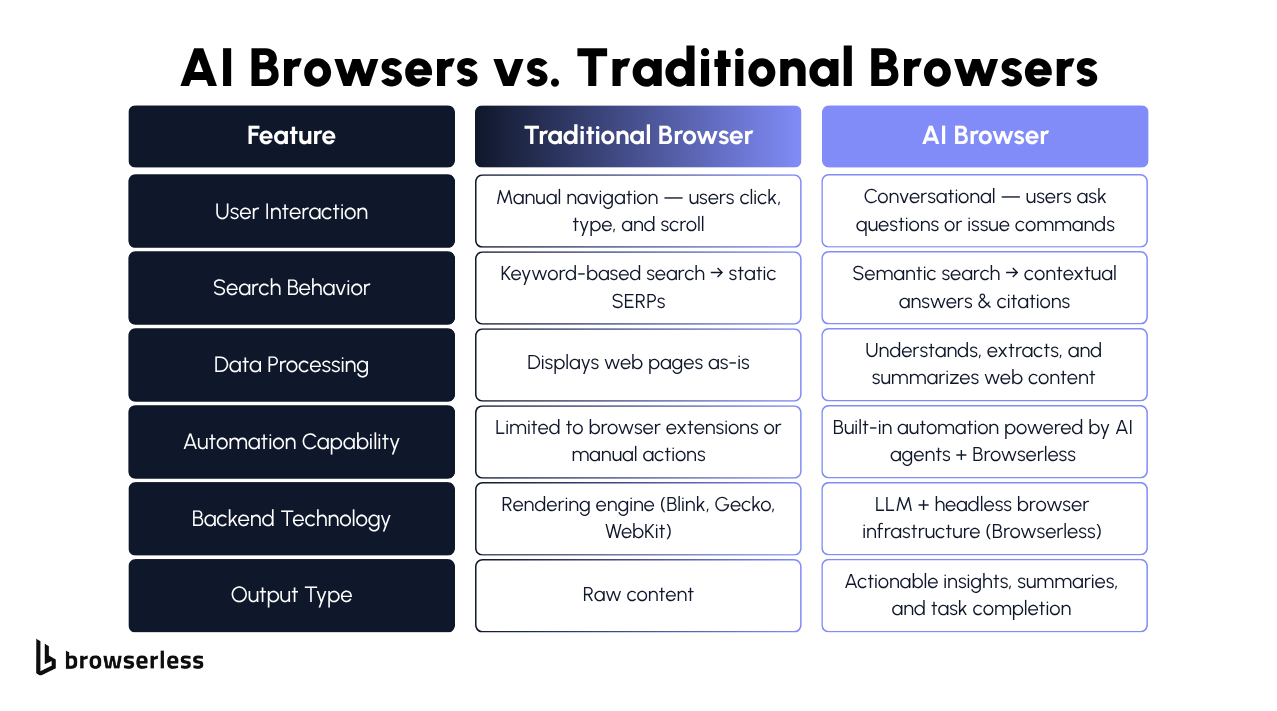
All of this depends on precise browser automation technology that allows AI systems to interact with the live web safely and efficiently. Platforms like Browserless give developers powerful APIs for managing and controlling headless browsers through endpoints such as /playwright, /chrome, /stealth and /chromium. These APIs let AI systems open web pages, extract data, and perform actions programmatically, without manual intervention.
Automation platforms also handle the tough parts of live browsing that users rarely see. They can solve CAPTCHA challenges, operate in stealth sessions that reduce ads and detection issues, and isolate every browsing session for safety.
These layers of control and precision enable user-facing AI-driven systems, such as Perplexity Comet and Microsoft Copilot, to interact manually with real-time websites rather than static archives.
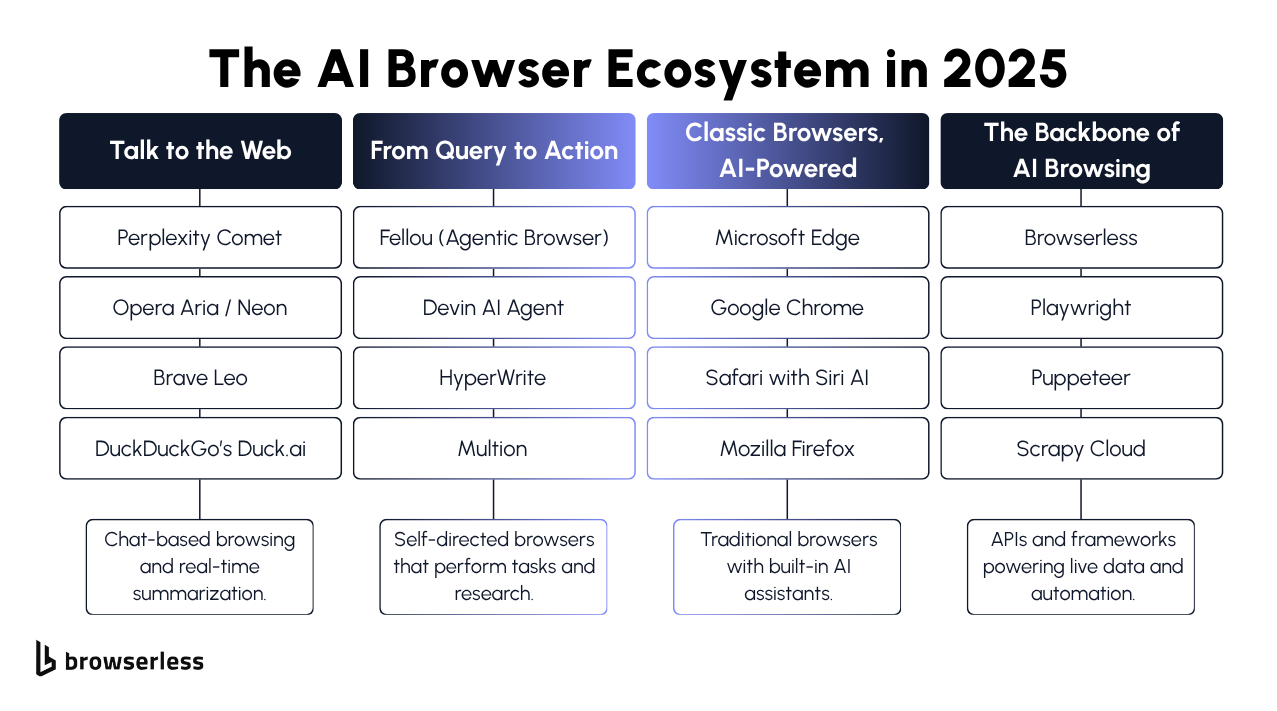
Comparing the Top AI Browsers in 2025
AI browsers have come a long way in just a year. What started as small add-ons or sidebar assistants has evolved into fully capable, intelligent browsers that can research, summarize, and even act for you. In 2025, several contenders are leading the charge, each with its own personality, strengths, and approach to blending AI features with everyday browsing. Let’s look at how the biggest names, Perplexity Comet, Opera Aria, Brave Leo, and Fellou compare, and what makes each one stand out.
Perplexity Comet
Perplexity Comet feels more like a personal AI assistant than a regular browser. You can ask it a question, highlight part of a web page, or even have it assist you in writing or continue your research automatically. It’s all conversational. Comet blends real-time web crawling with LLM reasoning to give you natural, sourced answers rather than just a list of links. It even provides citations so you can trace where the data came from, keeping results transparent and verifiable.
Under the hood, Comet uses live scraping layers (via Playwright and similar systems) to pull the freshest web content it can find. It also relies on semantic caching to save time on repeat queries, which keeps it fast even during heavy browsing sessions.
While it’s still early in its development, Comet is quickly earning attention from users who want a smarter, more interactive experience, something that feels less like just another browser and more like a true AI assistant.
Opera Aria and Neon
Opera Aria takes a different path. Instead of building an entirely new AI browser, Opera infused its existing one with smart AI features. Aria can summarize web pages, create images, and help you write or review content all without leaving your current tab. It’s conversational, responsive, and built directly into Opera’s interface, making it feel familiar to long-time users.
From a technical standpoint, Aria processes part of its data locally on your device, keeping your data encrypted and improving performance. It uses “edge-side” AI services to cut down latency, and a clever “context injection” system that sends relevant parts of a webpage to the AI model for summarization.
Meanwhile, Opera’s experimental Neon project explores more agentic browsing, where AI takes on small automation tasks on your behalf. Together, they’re quietly pushing the definition of what an AI browser can do without sacrificing privacy or speed.
Brave Leo and Microsoft Copilot Mode
Both Brave Leo and Microsoft Edge’s Copilot Mode have taken the “privacy-first AI” route, and for many people, that’s a big reason to try them. Brave Leo (learn more) is built right into the Brave browser and designed to summarize, analyze, and assist while keeping your data local.
It’s great for quick research, summarizing long articles, or asking context-aware questions about what’s open in your tabs. Brave’s focus is on local inference, so your queries don’t leave your machine, and your search history and passwords remain private.
Microsoft Copilot Mode (official site) brings that same concept to Edge, but with deeper ecosystem integration. It integrates with Microsoft Graph, Outlook, and Windows tools, enabling tasks such as document summarization, suggested next steps, and email assistance.
The AI can read your context across pages and apps, but you always stay in control, and nothing happens without your approval. Both of these browsers strike a balance between smart automation and personal privacy, giving users confidence while still expanding what AI can do inside the browser.
Fellou
Fellou is where things get really interesting. It’s not just a personal AI assistant that answers questions; it wants to take action. Fellou can plan and execute complex tasks across the web automatically.
For instance, you can request that it gather product data from various sites, complete forms, or even purchase once your preferences are confirmed. It works step-by-step using what’s called an “action graph,” where it maps out each move before executing it.
Behind the scenes, Fellou uses “agentic memory” to remember context, previous actions, and search history, allowing it to adapt to your work style. It’s designed to be transparent; you can always see what it’s doing on the internet and adjust before it proceeds.
For safety, it runs tasks in isolated sessions with tight control and encrypted data handling. It’s still early in development, but Fellou represents where many developers think the future of browsing is heading: a browser that doesn’t just help you read the web, it helps you perform work on it.
What AI Browsers Can Actually Do (and How They’re Built)
AI browsers are getting smarter fast. They don’t just open tabs or load web pages anymore; they actually understand what you want, gather the right data, and take action. Whether you’re doing research, tracking products, or automating daily tasks, these tools are becoming true AI assistants that work quietly in the background to make your browsing faster and more meaningful.
Everyday Use Cases for AI Browsing
- Research automation: AI browsers can summarize lengthy pages, extract key insights, and organize data into clean, organized reports. Instead of clicking through dozens of links, you can ask it to “compare these sources” or “find key takeaways,” and it’ll handle the work.
- E-commerce: They can watch prices, review listings, and alert you when something’s on sale or back in stock.
- Enterprise workflows: They log into tools, fill out forms, pull reports, and even trigger actions inside web apps, all without you lifting a finger.
What makes this possible is a mix of automation and language understanding. AI models interpret what you say, decide what to do, and then use web automation tools to carry it out accurately and in real time.
Here’s the quick breakdown of what’s happening behind the scenes:
- Browser automation orchestration enables AI systems to control live browsers, performing actions like clicking, typing, scrolling, and interacting in a human-like manner.
- Natural language action parsing turns plain requests into code-level actions (“extract contacts,” “save this page,” “run this search”).
- API-based data extraction tools like Browserless let the AI fetch structured info from websites, including dynamic JavaScript content, without relying on outdated scraping scripts.
All of this comes together so your AI browser can work smoothly across complex sites, handle context, and keep up with what you’re asking for.
The Future: AI Browsers to Agentic Web Agents
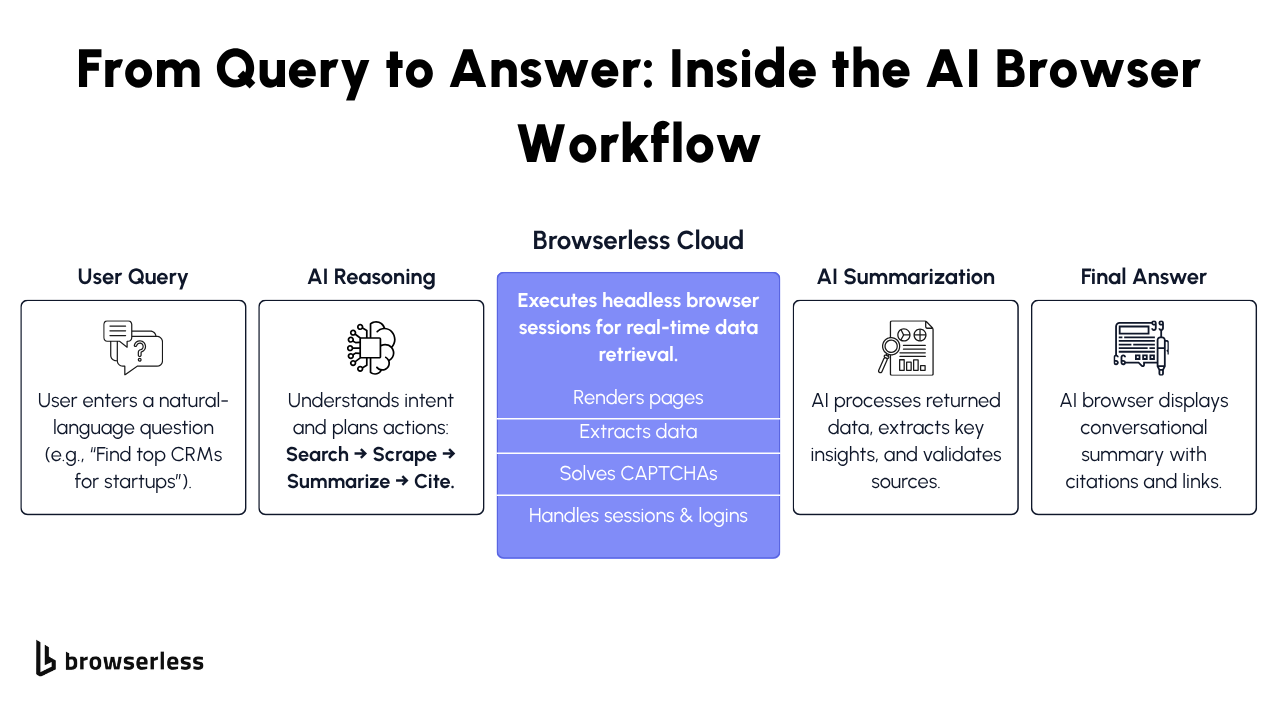
We’re reaching a turning point where browsers won’t just respond passively; they’ll begin acting on your behalf, planning and executing tasks across the web.
These are agentic web agents, and they represent the next major evolution of the AI browser. Below, I walk you through what that means, how it works under the hood, and how browserless automation fits into the picture.
Agentic Browsing Is the Next Big Shift
Agentic browsing refers to browsers (or agents integrated with browsers) that autonomously complete multi-step objectives for you. Instead of you manually browsing and clicking through pages, you might say:
“Research 3 best CRMs → compare their pricing features → fill out a signup form for the top choice.”
Behind that kind of capability lie a few technical approaches:
- Action chaining: The AI (usually an LLM) breaks your goal into sequential steps. Each step might be “open site,” “extract features,” “compare tables,” “fill form,” etc.
- Memory layers: To make the experience coherent across steps, the system tracks past search history, page context, user preferences, and results. Some systems call this “agentic memory.”
- Feedback loops: As the agent executes steps, it may re-evaluate, adjust its plan, or ask for user input when ambiguity arises. That keeps things safe and on-target.
This kind of agentic behavior enables the browser (or agent) to coordinate complex tasks across web pages, eliminating the need for you to micromanage each click or tab.
Browserless as the Backbone for Agentic Automation
Bridging decision-making and browser execution is a major technical challenge. That’s where browserless automation comes in. It provides agents with the tools to control real browsers, manage sessions, and scale across multiple parallel tasks.
- Multi-session orchestration: An agent might need to open multiple browser sessions simultaneously (checking several websites in parallel). Browserless lets you manage that seamlessly.
- Human verification fallback: When tasks are sensitive or ambiguous, the system can pause and allow a human to confirm before proceeding. This hybrid mode blends autonomy with safety.
- Real-time control APIs: Agents can interact with browserless endpoints to open pages, click, extract DOM content, or inject scripts exactly when they need to act.
- Ecosystem integration: Browserless ties into tools like LangChain, LlamaIndex, and Vercel AI SDKs, enabling agents to become “web-enabled” layers in AI pipelines.
- Event-driven triggers: Instead of running everything in batch, agents can listen for external signals (e.g., new data, webhooks) and spin up browser tasks as needed.
When agentic systems are built on top of browserless infrastructure, developers don’t have to reinvent the browser-control layer. They can focus on reasoning, planning, and crafting user experiences, supported by robust automation underneath.
Conclusion
AI browsers are changing the way we use the web, making browsing feel smarter, faster, and more natural. They blend language models, automation, and real-time intelligence so it feels like you’re working with an assistant, not just a tool. Browserless isn’t an AI browser itself, but it gives developers everything they need to build their own helping AI safely load pages, interact with sites, and actually get things done online. If you’re building your own AI browsing experience, give Browserless a try. You can sign up for a free trial and see how easy it is to give your AI the power to see, think, and act on the web securely and at scale.
FAQs
What makes an AI browser different from just another browser?
An AI browser isn’t just another browser; it’s designed to think, act, and adapt. Instead of simply opening web pages, it understands your intent and helps you perform tasks like research, summarizing, or comparing data automatically. Think of it as a personal AI assistant built into your browser, ready to act on your behalf. Modern browsers like Perplexity’s AI browser (Comet) or Microsoft Edge Copilot bring AI features that can summarize pages, manage tabs, and even help you create images or write faster.
Can an AI browser remember my search history or preferences?
Yes! Most AI browsers now maintain secure search history and context memory to make your browsing smarter. This means they can save your search history, remember which sites you like, and personalize how results appear. Privacy-focused options like Brave Leo and Opera Aria store this data locally, keeping it encrypted and safe on your device. Over time, your AI assistant learns how you browse without exposing your private data to the wider internet.
What are the most useful AI features in today’s browsers?
Today’s top AI browsers like Perplexity Comet, Fellou, and Opera Aria are full of smart AI features. You can summarize long pages, extract insights, create images, or even ask your AI assistant to send emails, collect research notes, or generate quick reviews. Some can perform complex tasks across multiple websites, like comparing products or analyzing data tables, all with a single click. These tools transform browsing from a task you perform into something the browser can do for you.
How does Browserless support AI browsers and automation?
Browserless powers much of the behind-the-scenes AI browser infrastructure. It provides developers with a means to remotely control headless browsers, such as Chrome, via APIs. That means AI systems can access live webpages, extract structured data, and execute real interactions like clicking, typing, or logging in securely. Browserless also supports multi-session orchestration, encrypted storage, and WebSocket control, making large-scale web automation safe, fast, and reliable. It’s what enables an AI assistant to explore the web as if it were a real human.
What kind of complex tasks can AI browsers perform right now?
Modern AI browsers can handle a surprising number of complex tasks. They can research, compare services, check reviews, fill forms, or even perform multi-step workflows automatically. For instance, Fellou’s agentic AI can execute actions like “find the top CRMs → compare pricing → start a trial,” all in one session. AI browsers can also manage tabs, log in to apps, and save progress, allowing you to focus on decisions while your AI assistant handles the work in the background.